- free
- bundle
- top rated
Kilohearts Essentials is a free collection of extremely useful effects which can be used as regular plugins in your DAW or loaded as Snapins in any Kilohearts Snapin Host.
All your Essential Effects - for FREE!
Kilohearts Essentials includes all the basic, and many not-so-basic, effects for everyday sound design and mixing in any DAW. The unified design will ensure optimal workflow, whatever project you are working on.
A Growing Collection - Kilohearts intend to continue adding high-quality plugins to the Kilohearts Essentials bundle at no extra cost, so your options will continue to expand in the future. New licenses will be added to your account as soon as they are released.
Part of the Kilohearts Ecosystem - If you own any of Kilohearts' Snapin Host plugins (Phase Plant, Multipass, or Snap Heap) all these effects are immediately available for you to combine and modulate to your heart's desire with them. With Kilohearts' advanced modular ecosystem, a universe of possibilities awaits.
Created by Experienced Developers - At every point in the signal chain, all Kilohearts software is optimised for the highest quality audio generation and processing with the lowest possible CPU load. For professional music production and sound design, you won’t ever have to worry about shortcomings in sound quality again.
Lifetime Free Updates - Once you buy a license for any Kilohearts plugins you will get all future updates for free. You won’t be charged a penny for new versions and Kilohearts will continue to improve their software with new features and OS compatibility (yes, it’s all M1 Native already!), which means investing in Kilohearts software is a very sensible move for the serious sound designer.
Plugins Included
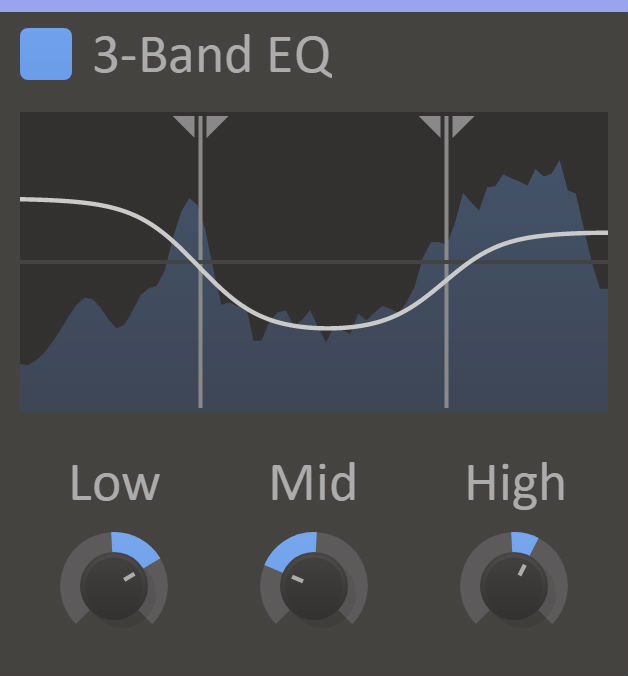
3-Band EQ
Kilohearts' filters are always awesome, and stacking them together to create a quick 3-band EQ just made them even easier to use.
3-band EQ will get you surprisingly far when it comes to shaping your sound, or your entire song. By dragging the split frequencies around it feels like much more than a standard 3-band equalizer.
Features
- Low - Set the gain of the low frequencies.
- Mid - Set the gain of the frequencies in between the low and high threshold.
- High - Set the gain of the high frequencies.
- Spectrum Split Lines - Drag the lines to set the low and high-frequency thresholds.
- Settings Panel - Whenever you have your mouse cursor over a snapin there is a small arrow at the top right corner. It opens a settings panel where you handle presets. It also has a "randomize" button that can be useful.
- Enabled Checkbox - The small checkbox to the left of the plugin name is a checkbox that bypasses the effect when disabled.
- Resize Handle - The bottom right corner of all Kilohearts plugins is a resize handle for scaling the UI to any size. This allows you to get a good view of the controls whatever the screen resolution, and also comes in handy if you need big controls, e.g. when using 3-Band EQ as a real-time effect on a touchscreen monitor during a live set. (This is not available when the snapin is used inside a snapin host.)
Get more out of 3-Band EQ!
3-Band EQ shines on its own, but it was primarily created to power up the different "Snapin Hosts" Kilohearts offer. These are bigger effects units that utilize all the available snapins and give you a really fun and creative workflow for combining them in any way you can think of. So have a look at Snap Heap and Multipass right now!
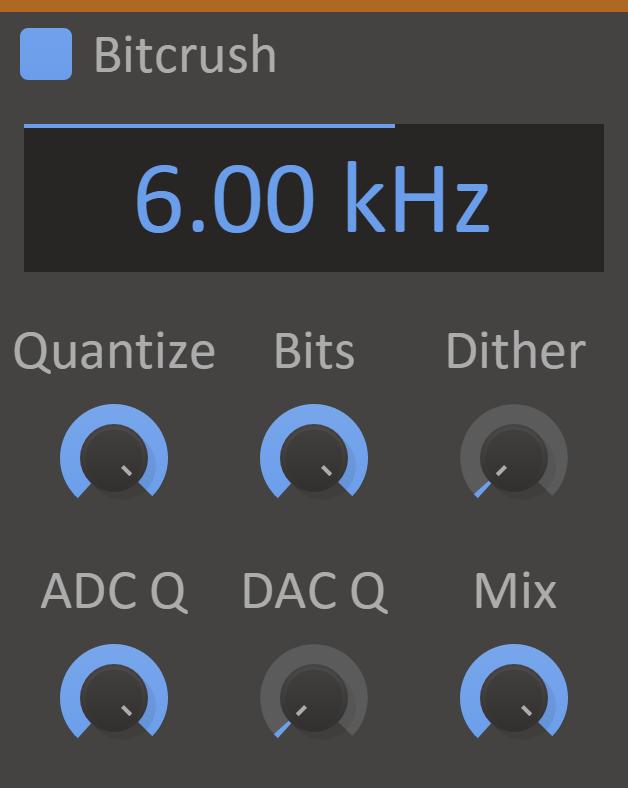
Bitcrush
When nostalgia hits, Bitcrush can bring you back to the digital hardware of times past. It simulates the audio being played back using a low-quality sampler with a limited sample rate and bit depth. Mm, crunchy.
Bitcrush can be used to create distorting effects that sound like that of scraping analog radio, or inherently lo-fi sound sources, like old video games.
Features
- Rate Display - Down sample the signal to a minimum of 200 Hz.
- Bits Knob - Quantize the amplitude of each sample of the signal. A lower value will result in a more distorted sound.
- ADC Q Knob - Quality of the analog-to-digital conversion. A lower value will add dissonant aliasing in the low frequencies.
- DAC Q Knob - Quality of the digital-to-analog conversion. A lower value will add dissonant aliasing in the high frequencies.
- Dither Knob - Adds noise to the signal in order to reduce distortion caused by quantization.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
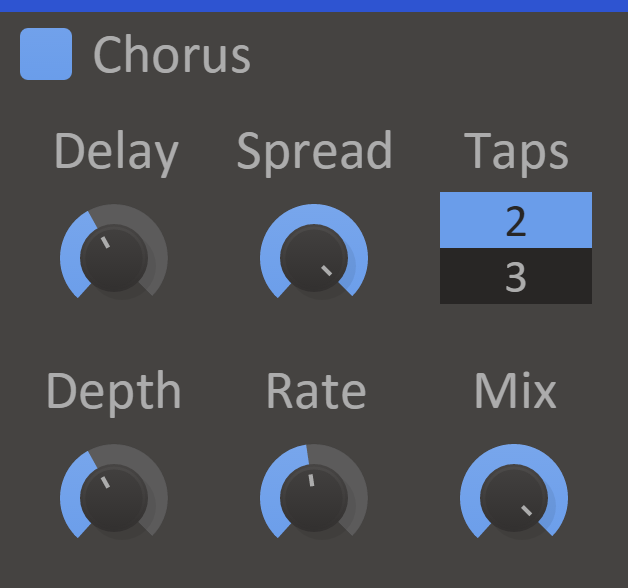
Chorus
Chorus enhances the stereo effect and presence of a sound by mixing it with delayed versions of itself. It's like your own personal choir!
Features
- Delay Knob - The average delay for the delayed voices.
- Rate Knob - The frequency of how fast to vary the delay.
- Depth Knob - How much to vary the delay.
- Spread Knob - Stereo width of the effect. A lower value will go towards a mono output.
- Taps - The number of chorus voices.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
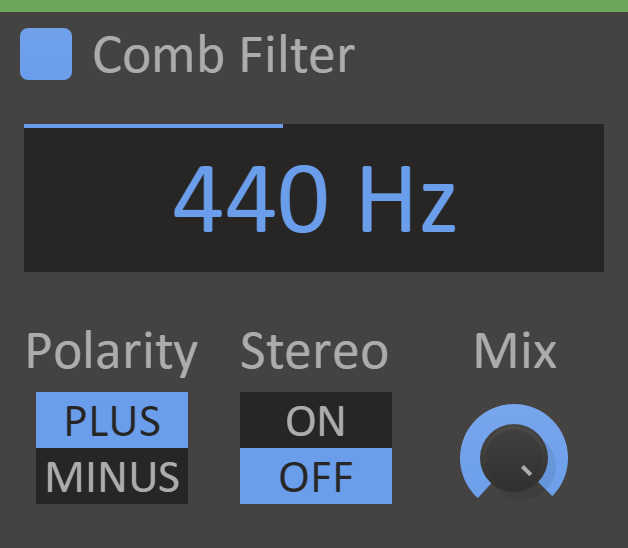
Comb Filter
The Comb Filter hollows out the sound by carving out frequencies at each multiple of the base frequency, like the teeth of a comb.
The Comb Filter will mix the signal with a delayed version of itself, creating a filter with repeated troughs and peaks across the spectrum.
It's also possible to process left and right differently in a way that not only gives a wide stereo effect but also collapses right back to the original signal when mixed to mono. Nifty!
- Cutoff Display - Cutoff setting for the filter, the distance between each peak.
- Polarity - The polarity setting swaps troughs for peaks and vice versa, with the plus setting having a peak at 0 Hz, and the minus setting a trough at 0 Hz.
- Stereo - The stereo setting flips the polarity setting for the right channel, allowing the comb filter to be used for mono-compatible stereo widening.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
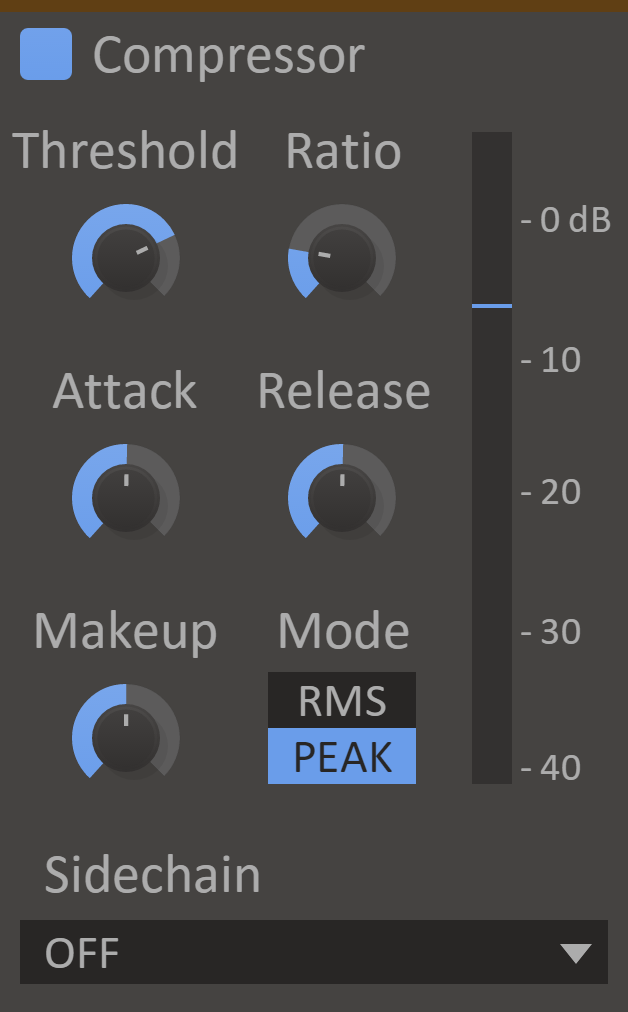
Compressor
Someone somewhere once said that there are 931 compressor plugins in the world. Well, now there's 932!
A compressor will even out the audio volume by lowering the volume when the signal is loud. This helps shape the dynamics of the sound both at the initial attack and the sustain tail. Each compressor has its own flavour, and this Compressor tastes sweet.
Features
- Attack Knob - The attack time is the time it takes to lower the volume when the input volume is over the threshold.
- Release Knob - The release time is the time it takes to return the volume to normal when the input volume is under the threshold.
- Mode - In RMS mode the compressor will measure the volume using the root mean square method, which gives an accurate measurement of audio power. In peak mode, the compressor will follow the peaks in the audio waveform, which makes it more responsive to transients.
- Ratio Knob - The ratio decides how much the compressor will reduce the audio volume. At 1:2, for example, the volume will be lowered until it is halfway between the input volume and the threshold.
- Threshold Knob - The threshold for when the compressor will start lowering the volume.
- Makeup Knob - The makeup gain will increase the volume of the output signal to compensate for the loss in overall volume that the compressor causes.
- VU Meter - Displays the current input level, the selected threshold, and the compressor's current attenuation.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
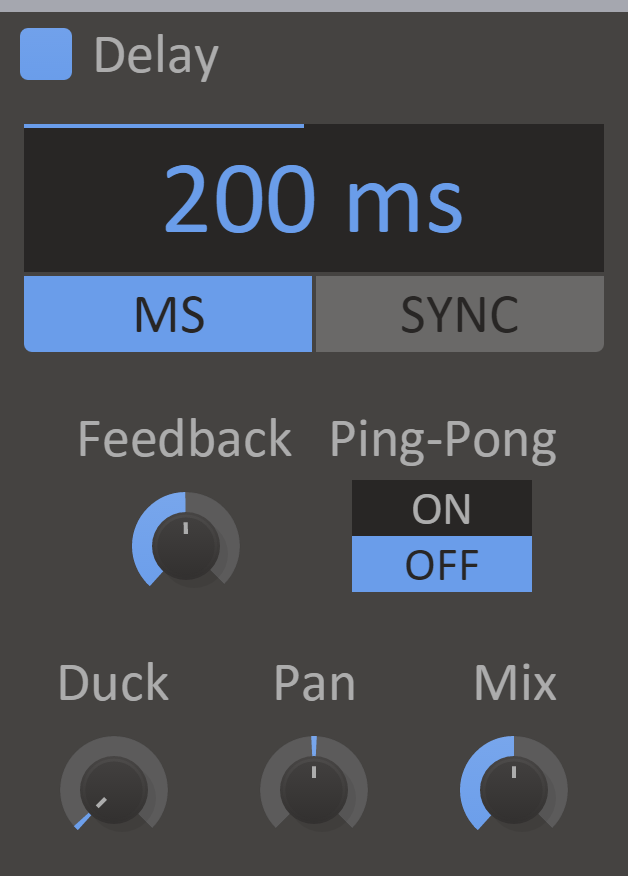
Delay
While large echoing cavernous chambers seldom are the first pick for a good acoustic space, Delay effects have been ubiquitous in sound processing for a long time.
Delay can be run both free-running and tempo-synced with various stereo and feedback options. Most notable however is the duck feature, which optionally only lets the echoed sound through when there is no dry input signal. This allows for a long and heavy delay while still avoiding clutter over the original sound. Clever!
Features
- Delay Display - The amount of time before the delayed sound starts playing. This will be expressed in milliseconds or as parts of a beat, depending on Sync Mode.
- Sync Mode - When sync is enabled the delay time will be synchronized to the song tempo.
- Feedback Knob - The feedback setting will cause the delayed sound to feedback into the delay. This will create an exponentially decaying echo.
- Pan Knob - Adjust the panning of the delayed sound.
- Ping-Pong - Swaps the left and the right channel of the delayed sound when it is fed back into the delay. When combined with panning this will make the echo bounce back and forth between the speakers.
- Duck Knob - When duck is turned up, the output volume from the delay will automatically be lowered when the input volume is high.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
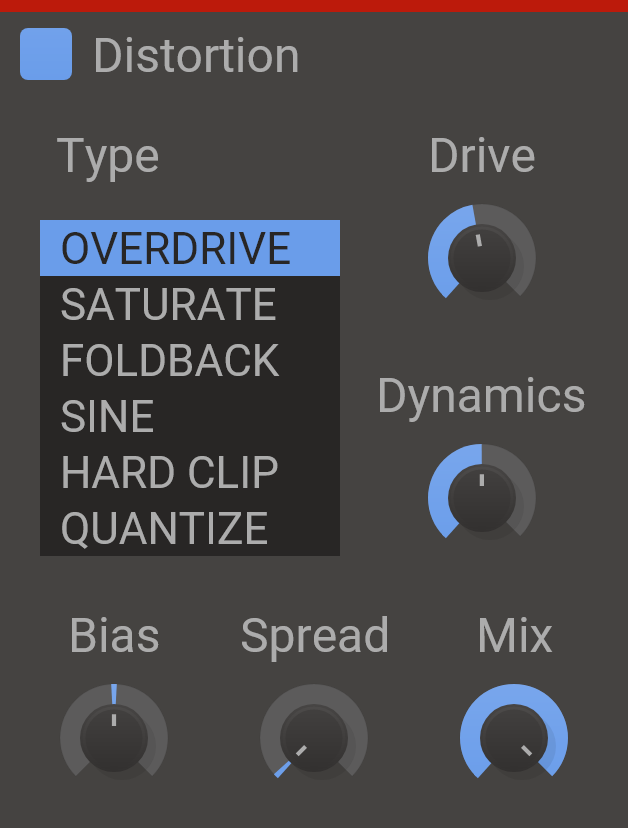
Distortion
Ever since mankind invented music, there has been a desire to make it heavier. Distortion can take your sound from zero to a sword-wielding hero in seconds.
5 different distortion shapes are available to add a tinge of edge or rip things apart. In stereo, if that's what you're into.
Features
- Drive Knob - The drive setting will boost the input signal, causing a heavier distortion.
- Bias Knob - The bias will add a DC offset to the signal before distorting. Adding some bias can prevent the distorted audio from sounding hollow and uninteresting.
- Spread Knob - The spread will add different amounts of bias to the left and right channels. This can give some nice and subtle stereo widening.
- Type - The flavour of distortion. Select between overdrive, saturate, foldback, sine and hard clip.
- Dynamics - A common problem with distortion is that it can remove the dynamic content of the input signal, forcing the output to maximum volume. Turn up this knob to preserve the dynamics of the input.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
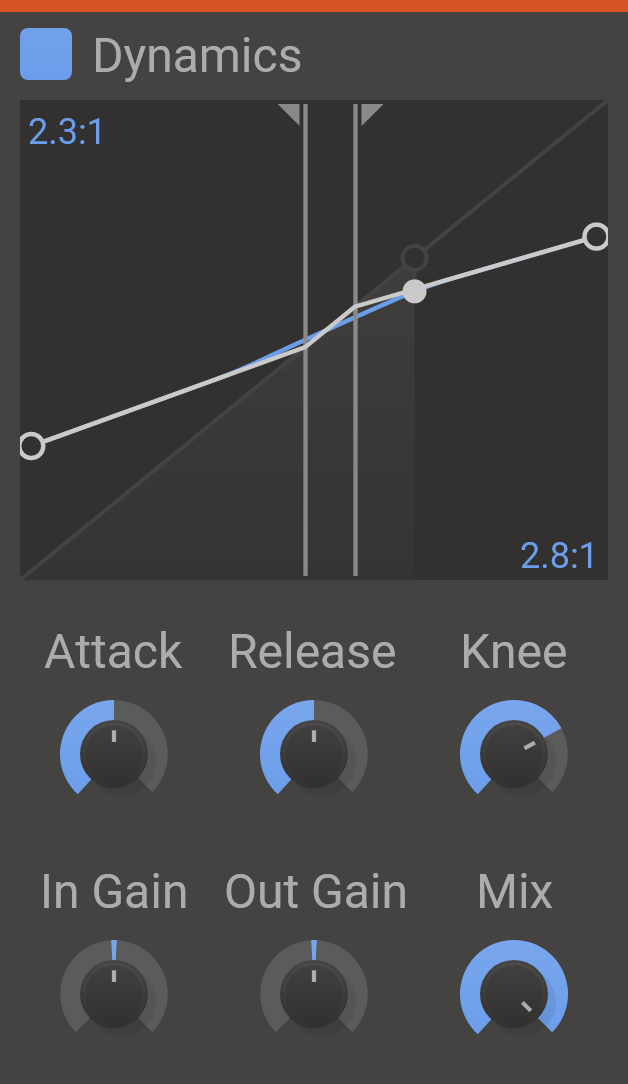
Dynamics
Keeping your levels in check was never easier.
Dynamics can be used to give an aggressive oomph to your leads. Try it in Multipass for multiband processing.
Dynamics processing features upward and downward compression as well as expansion. Thresholds and ratios are controlled by clicking and dragging on the visualization in the upper part of the plugin interface. The visualization shows how input levels are mapped to output levels by the dynamics processing. The current input and output levels are marked in the visualizer by a moving disc.
Features
- Low Threshold - Low threshold for upwards compression and expansion.
- Low Ratio - Ratio of upwards compression or expansion below the low threshold.
- High Threshold - High threshold for downwards compression.
- High Ratio - Ratio of downwards compression above the high threshold.
- Attack - Adjusts attack time.
- Release - Adjusts release time.
- Knee - Smoothes the knee of the compression curve across the thresholds.
- In Gain - Adjusts gain for the incoming signal.
- Out Gain - Adjusts gain after compression.
- Mix - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
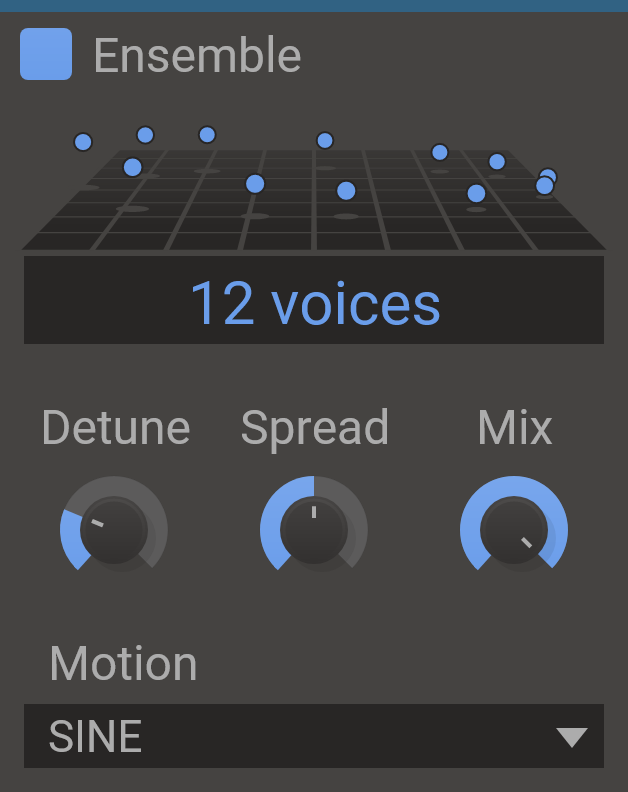
Ensemble
Make multitudes from each moment.
Ensemble is a silky-smooth way to turn one voice into a crowd.
Like a chorus effect, Ensemble creates and plays back delayed copies of a sound to generate additional unison voices. But beyond this, it modulates the phase of each voice to avoid the metallic flanging of near-identical waves, which means a truly natural group sound from a single source.
Features
- Voices - Number of voices to play simultaneously.
- Detune - How quickly to modulate the delay for each voice, affecting how detuned the voices will be.
- Spread - Pans voices left or right for a stereo effect.
- Mix - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Motion - Selects between different patterns for the modulations of the voices.
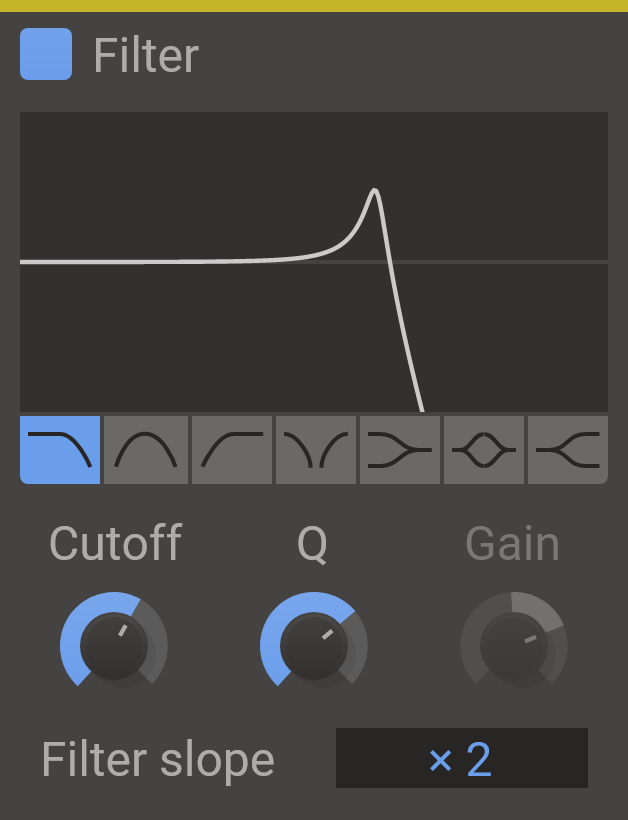
Filter
Sometimes in life, sound comes with frequencies you don't like. So why not cut them out?
Filter is a resonant filter with 7 modes, swiftly getting rid of frequencies you don't like or enhancing frequencies you do. And it's doing it and doing it and doing it well.
Features
- Type - The type of filter. Select between low pass, bandpass, high pass, notch, low shelf, peak and high shelf filters.
- Cutoff Knob - The operating frequency of the filter. In a low-pass filter, this is the frequency where the signal is reduced by 3dB.
- Q Knob - The filter Q setting. High values for Q will make the filter resonate at the cutoff frequency.
- Gain - The gain value for the low shelf, peak and high shelf filter types.
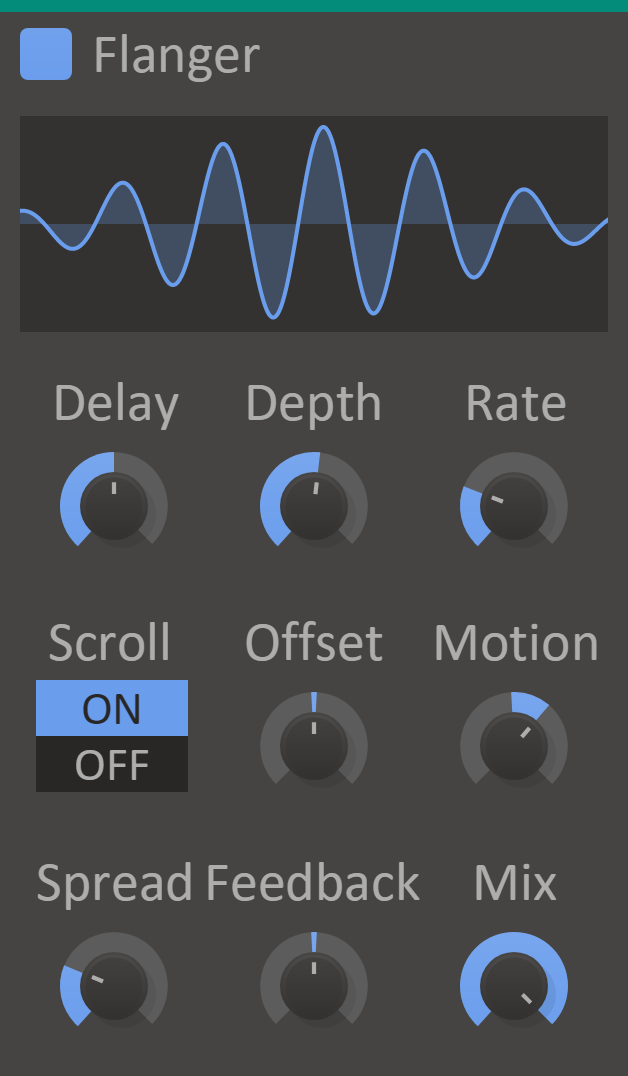
Flanger
Create weirdly cyclic motion in your sound with Flanger.
It's sort of similar to a sweeping comb filter.
Flanger Creates a flanging effect by mixing the audio with a slightly delayed version of itself. The length of the delay can be adjusted manually and modulated. Optionally, this effect can also add a phase shift between the dry and wet signals to create an infinite barber pole-style flanging effect upwards or downwards.
Features
- Delay - Adjusts the minimum delay.
- Depth - Depth of delay modulation. Added on top of the minimum delay set by the delay knob.
- Scroll - Enables the phase offset and motion functions of the effect.
- Spread - Stereo spread between left and right channels. Affects delay modulation and phase offset.
- Rate - Rate of delay modulation.
- Offset - Phase offset between dry and wet signals.
- Motion - Rate of modulation for the phase offset.
- Mix - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Feedback - Feedback of the wet signal back into the delay line.
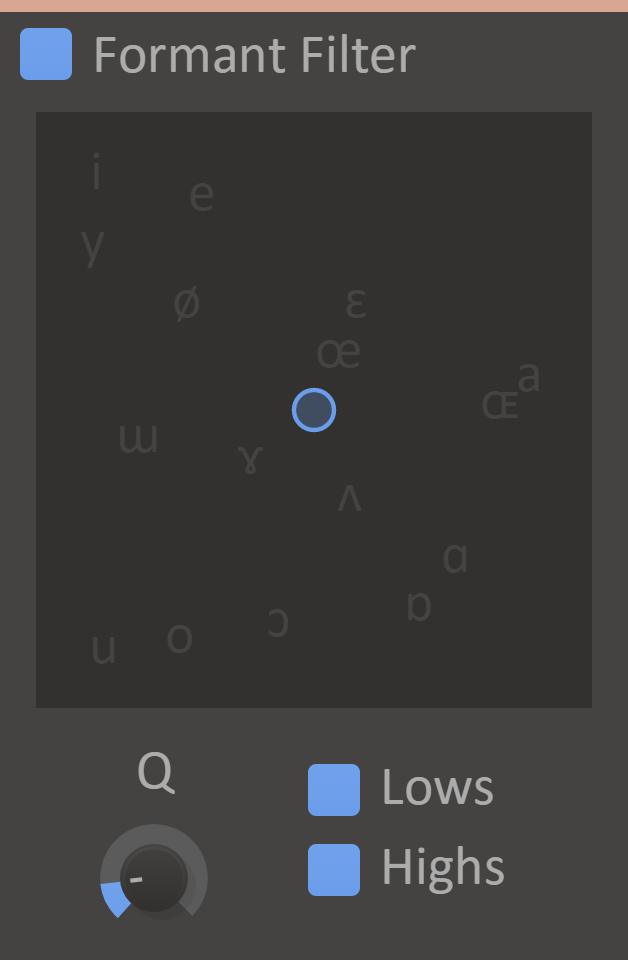
Formant Filter
If your music doesn't get enough "Aahs" and "Oohs", maybe you should try putting them into the actual music? Formant Filter shapes the sound in a similar way to how the vocal tract works, leading to vowel-esque sounds. So, channel your inner robo-Tarzan. Aaaaoooeoeeeoeeeee!
The Formant Filter will boost two frequencies to mimic the sounds of different vowels.
Features
- Vowel Selector - Selects two frequencies to boost. We've put the phonetic symbols of some common vowel sounds on the selection pane. Applying an LFO modulation to either axis of the pane can give some nice human-esque qualities to your sound.
- Q Knob - Adjust how powerful and narrow the frequency boost is.
- Lows - Allow low frequencies through the filter.
- Highs - Allow high frequencies through the filter.
Frequency Shifter
Do you ever think to yourself: "Screw harmonics!"? Well, ok, probably not. But let's do it anyway!
Frequency Shifter will shift all the frequencies in the input signal up or down by a certain amount. This kind of shifting will ruin the harmonic content of the input signal, making it sound dissonant. Mmm... Dissonance...
Features
- Shift Display - How much to shift all frequencies by.
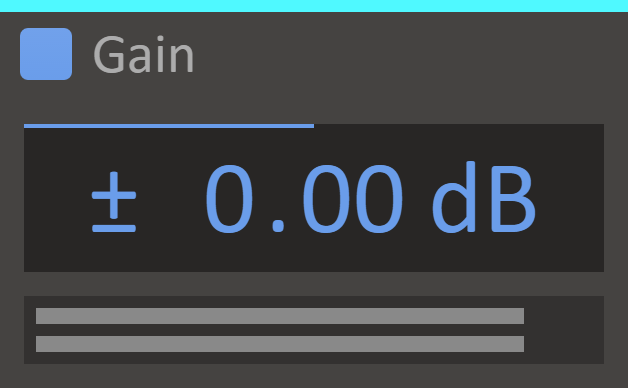
Gain
Sound loud? Make softer. Sound quiet? Make louder.
Features
- Gain Display - Set how much to increase or decrease the volume, in decibels.
- VU Meter - Displays the current output level on the left and right channels.
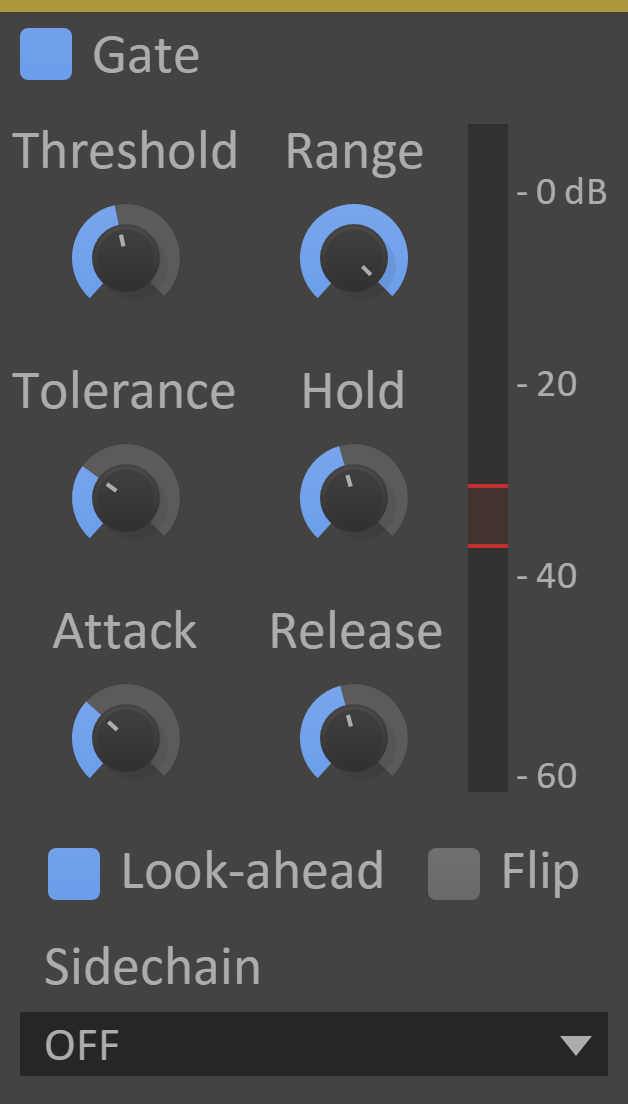
Gate
Not all sound is created alike, and sometimes you want to just leave it at the Gate. Quickly cut out low hum and noise from the signal, cut reverb tails short or exaggerate the dynamics in a beat. The possibilities are... maybe not endless, but should cover your gating needs!
Gate has simple but powerful controls for tuning in the desired effect, and can easily be driven by an external sidechain signal. The gate can also be flipped around to make a signal duck under another.
Features
- Attack Knob - The attack time is the time it takes to for the gate to fully open when the input volume is over the threshold.
- Hold Knob - The hold time is the minimum time the gate will stay open.
- Release Knob - The release time is the time it takes to for the gate to fully close when the input volume is under the threshold.
- Threshold Knob - The volume threshold for when the gate will open.
- Tolerance Knob - A hysteresis range requiring the volume to drop a set amount of dB under the threshold before closing.
- Range Knob - The amount to attenuate the signal when the gate is closed.
- Look-Ahead - When enabled, a 5ms look-ahead will be used, allowing transients through at the cost of latency.
- Flip - When flipped, the gate will act in reverse attenuating the signal when the gate is open.
- VU Meter - Displays the current input level, the selected threshold and tolerance, and the gate's current state.
- Sidechain - When you select another sound source in the sidechain drop-down the plugin uses that source for determining the behaviour of the plugin instead, it still affects the main sound source. This is useful for lowering a lead sound whenever the kick hits. Remember the song Call on Me by Erik Prytz? It has a lot of sidechaining going on.
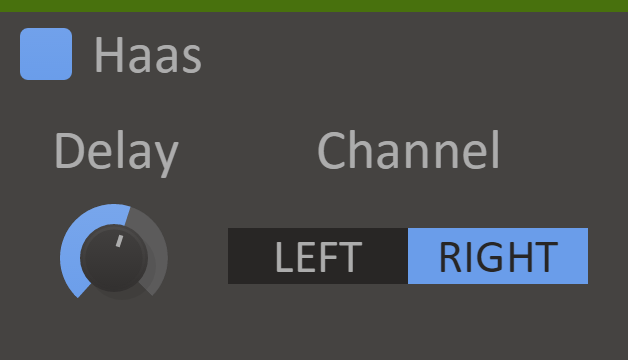
Haas
Panning sound is key in mixing and sound placement, but amplitude is only part of how humans determine the direction of sound. The Haas effect targets another mechanism that detects small differences in time between left and right to position sound.
The HAAS effect will widen the stereo of the audio by delaying the left or the right channel slightly.
Bottom line, it brings stereo width to sounds where there previously was none. Simple as that.
Features
- Channel - Which channel to delay.
- Delay Knob - The delay time.
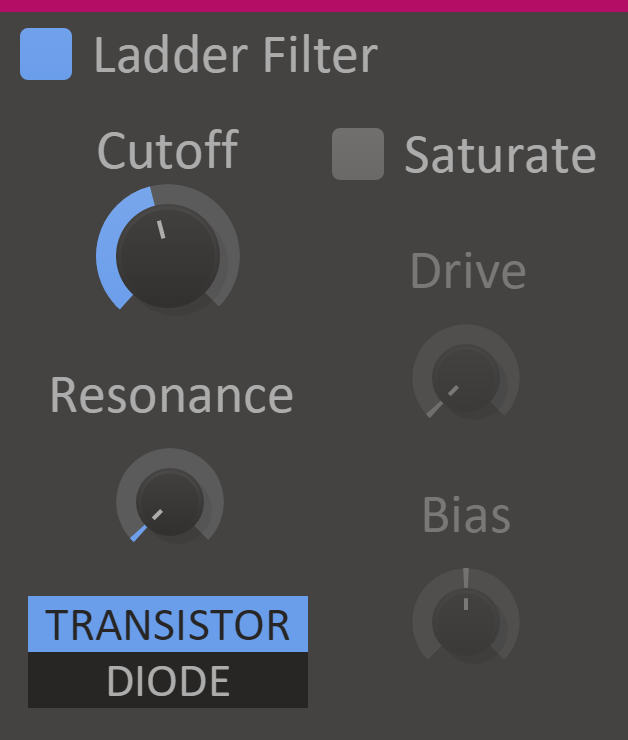
Ladder Filter
When you're looking for a bit of that vintage feel, Ladder filter will twist your basses into squelching retro-licks akin to those of the Moog or the 303. Crank the drive up an extra notch and it will even function as a warm distortion. Mmm, smooth.
The Ladder Filter simulates low pass filters found in classic hardware synths.
Features
- Cutoff Knob - The filter cutoff frequency.
- Resonance Knob - The filter resonance setting. High values will make the filter resonate at the cutoff frequency.
- Topology - Selects between transistor ladder and diode ladder topology. The diode ladder has a slightly more gentle roll-off after the cutoff frequency. The two topologies also behave differently when saturation is enabled.
- Saturate - Simulates saturation of electronic components in the filter.
- Drive Knob - Simulates overdrive of the components. Only available in "Saturate" mode.
- Bias Knob - Simulates bias voltage over the components. Only available in "Saturate" mode.
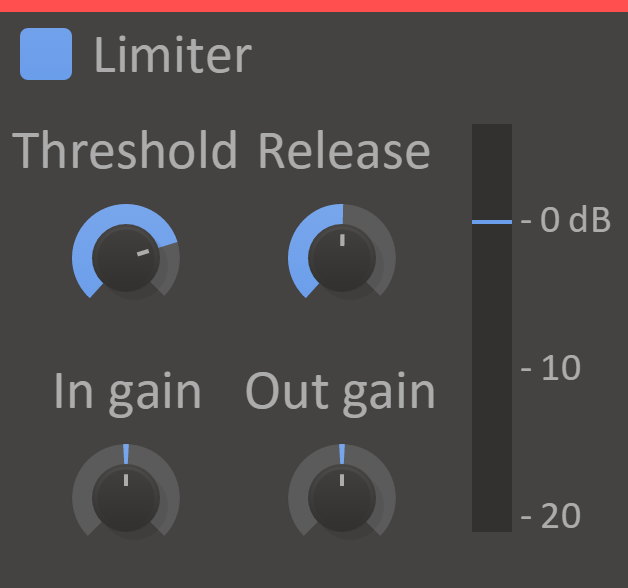
Limiter
Whether you want to crank the last drops of gain out of your track or just want to control a few loud peaks, a Limiter can be the weapon of choice.
By looking a little bit into the future, a limiter can make sure your signal never goes louder than you want it to without distorting or destroying transients. Even with the knob turned to 11.
Features
- In Gain Knob - Gain to apply to the input signal before limiting.
- Out Gain Knob - Gain to apply to the input signal after limiting.
- Threshold Knob - The maximum allowed volume.
- Release Knob - The release adjusts how quickly the limiter returns the volume back to normal after limiting it due to a peak in the input volume.
- VU Meter - Displays the current input level, the selected threshold, and the limiter's current attenuation.
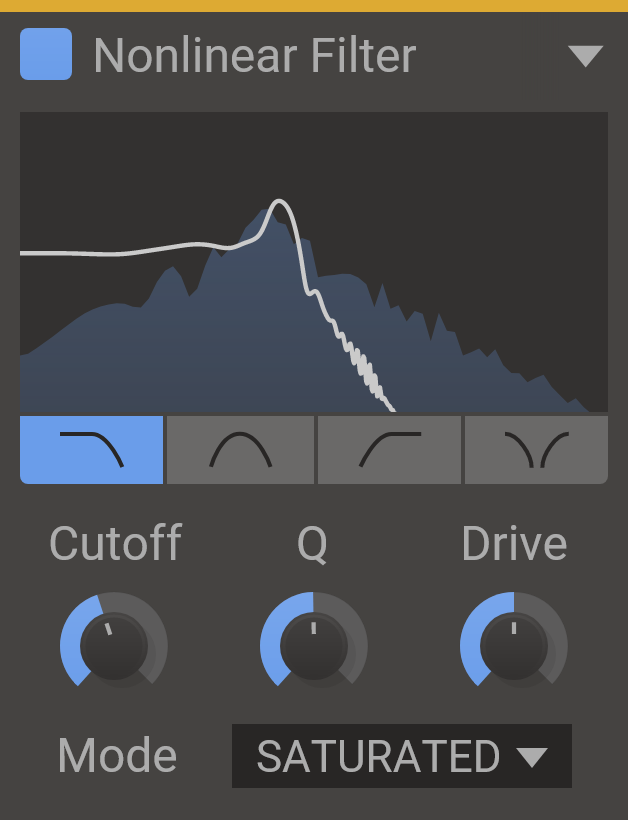
Nonlinear Filter
The nasty way to sculpt and refine your sounds.
Do you know how Jimi Hendrix got his signature guitar sound? Nonlinear Filter.
Or that screechy lead in Block Rockin' Beats, by The Chemical Brothers? Nonlinear Filter.
How about the synth melody in Madonna's Like a Virgin? Believe it or not, Nonlinear Filter.
Alright, maybe not Kilohearts Nonlinear Filter. But if you are looking to add some vintage analog twang to your sound, we have you covered. Nonlinear Filter offers colourful filtering in a variety of flavours, ranging from a classic analog sound to more outlandish modes the further down the list you go.
Features
- Type - Select between low pass, bandpass, high pass and notch filters.
- Cutoff - The operating frequency of the filter.
- Q - The filter Q setting. High values for Q will make the filter resonate at the cutoff frequency.
- Drive - Overdrives the filter, which makes the effect of the nonlinear behaviour more prominent.
- Mode - Select what flavour of nonlinearity you want. The clean mode has no nonlinearities and does not colour the signal. All other modes distort and colour the signal in different ways to some extent.
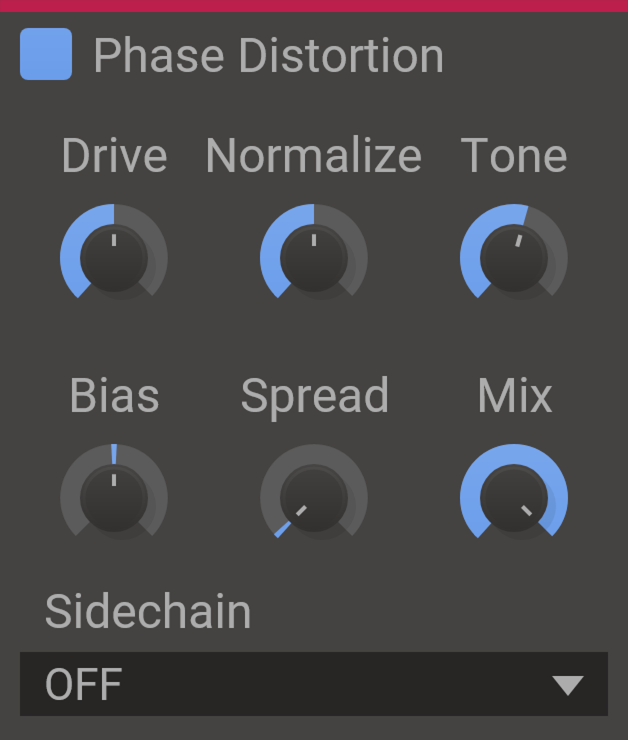
Phase Distortion
FM but as an effect?
Are you tired of only warping signal amplitude like a pleb? Phase Distortion is here to deliver phase melting mayhem!
Traditionally, most distortion units overdrive and shape the amplitude of a signal in various ways to generate a rougher sound. Phase Distortion instead lets the signal modulate the phase of itself, essentially resulting in something similar to feedback FM. This way you can add that FM touch to any sound, to get a sweet 80s vibe or a filthy dubstep bass.
Will you use your newfound power for good or for evil?
Features
- Drive - Controls the amount of distortion.
- Normalize - Normalizes the signal, making the effect insensitive to input gain.
- Tone - Filters the modulation to reduce high-frequency noise.
- Bias - Adds a constant phase offset to all harmonics.
- Spread - Spreads phase offset for left and right channels for a stereo effect.
- Mix - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Sidechain - Allow a secondary input to control the phase shift amount.
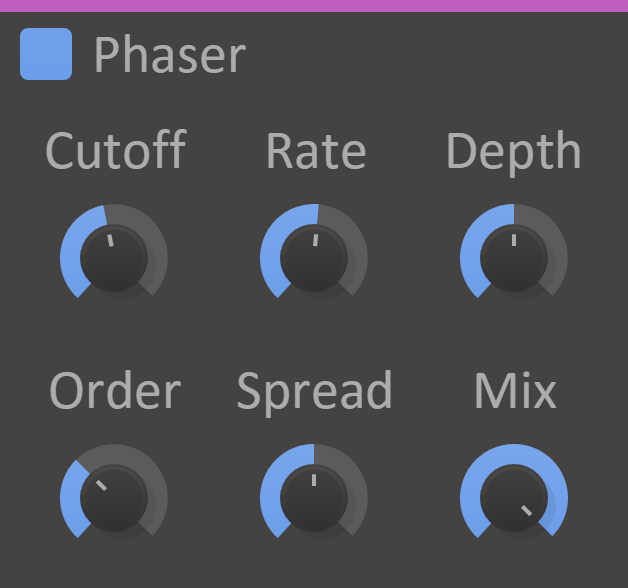
Phaser
Beam me up, Scotty! No matter if you set the knob to stun or kill, Phaser can spice up your life with twirly frequency sweeps.
The Phaser will filter the input signal, creating a series of moving peaks and troughs in the audio spectrum.
Pretty much all the bad things with signal phase issues, but turned into an effect and labelled "cool".
Features
- Order Knob - A higher-order setting will increase the order of the filters used by the phaser, creating a more pronounced effect with more peaks and troughs.
- Cutoff Knob - Sets the cutoff of the filters in the phaser, moving the peaks and troughs in the audio spectrum.
- Depth Knob - Adjusts the depth of modulation of the cutoff.
- Rate Knob - Adjusts the rate of modulation of the cutoff.
- Spread Knob - Adds a phase offset for the cutoff modulation between the left and right channels, for a stereo widening effect.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
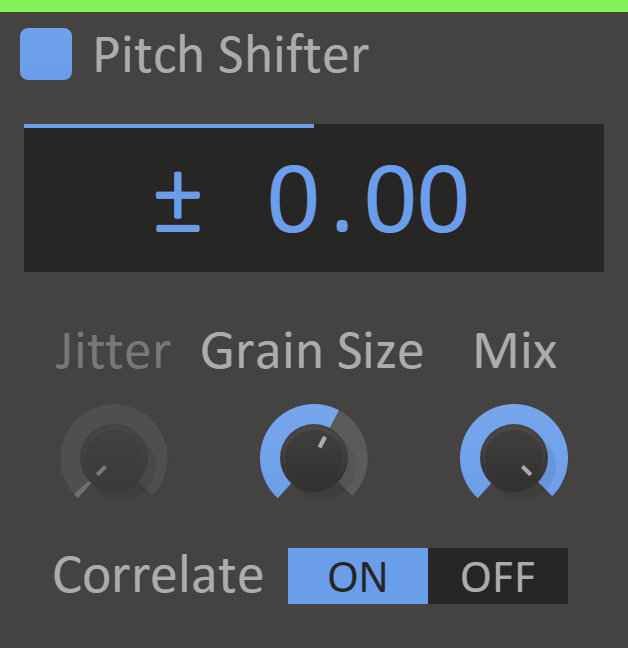
Pitch Shifter
Are you out of tune? Do you want to be? Either way, Pitch Shifter uses grain delay to bring the pitch where you want it to be. Or at least somewhere else from where it already is.
The Pitch Shifter will adjust the pitch of the input signal up or down.
Features
- Pitch Display - How much to adjust the pitch, in semitones.
- Jitter Knob - How much randomness to add to the pitch. A high jitter setting can give a unison-like effect. This is only available when Correlate is off.
- Grain Size Knob - During processing the pitch shifter chops up the audio into small snippets called grains. This setting adjusts the length of the grains, which can influence the sound.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Correlate - Enables a more advanced algorithm resulting in a more clear effect for many inputs. Be careful though as it might have problems with complex pads and textures.
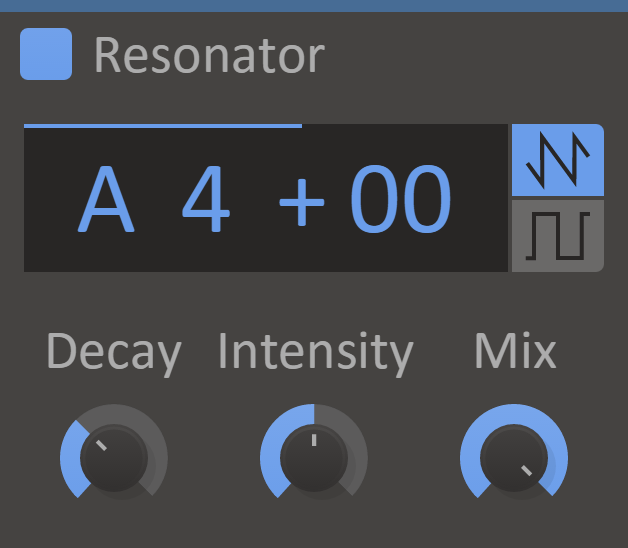
Resonator
Found a frequency that you really really like? Want it to hang in there for just a little bit longer? Let it ring in the new year with Resonator.
Specific frequency harmonics in the input sound are enhanced and propagated, giving you fine control over the sustain of a tone.
Features
- Pitch Display - The frequency at which to resonate.
- Decay Knob - Sets how long it takes for the resonance to ring out after the input goes silent.
- Intensity Knob - Adjusts how much the resonance amplifies the input signal.
- Timbre - Switches between two different harmonic series for the resonance. Choose between all harmonics (saw tooth wave) or odd harmonics (square wave).
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
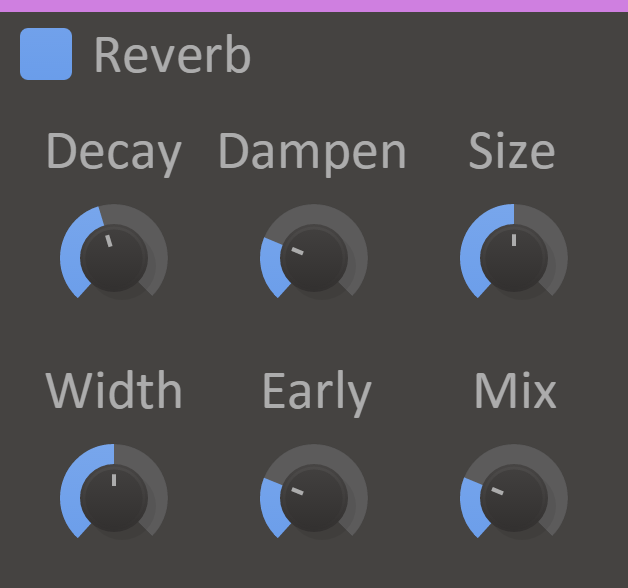
Reverb
Reverbs, simulating the millions of tiny echoes that naturally bounce off the walls in a room, play a central part in glueing together sounds in a song. There are likely few tracks today that don't contain reverb in any form.
Features
- Decay Knob - The reverberation time, i.e. the time it takes for the reverb to go silent after sound has passed through it.
- Dampen Knob - Adds damping to high frequencies so that they decay faster than low frequencies.
- Size Knob - Adjust the size of the virtual room that reverb simulates. Ranges from closet to church.
- Width Knob - Adjusts the stereo width of the reverb. At 100% the left and right channels are completely uncorrelated in the wet sound.
- Early Knob - Adjusts the balance between early and late reflections. A higher value will give a brighter and more responsive reverb.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
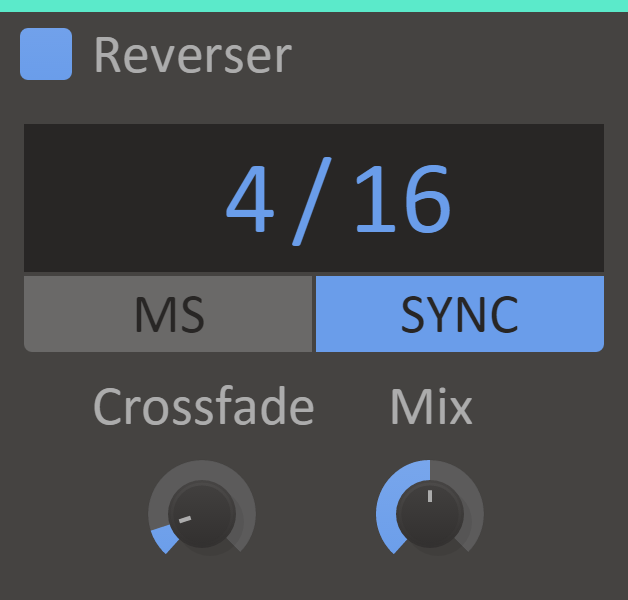
Reverser
Remember in The Ring when Samara kind of walks backwards but still towards you and it's all scary and weird? This is not really like that.
However, Reverser does delay and reverse sections of the input sound resulting in anything from hauntingly eerie textures to reverse percussion hits.
Features
- Delay Display -The amount of time before the delayed sound starts playing. This will be expressed in milliseconds or as parts of a beat, depending on the Unit setting.
- Delay Time Unit - When Unit is set to 'Sync' the delay time will be synchronized to the song tempo.
- Crossfade Knob - Time to ramp in/out the reversed audio to avoid any clicks and pops, in per cent of the reversed section length.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
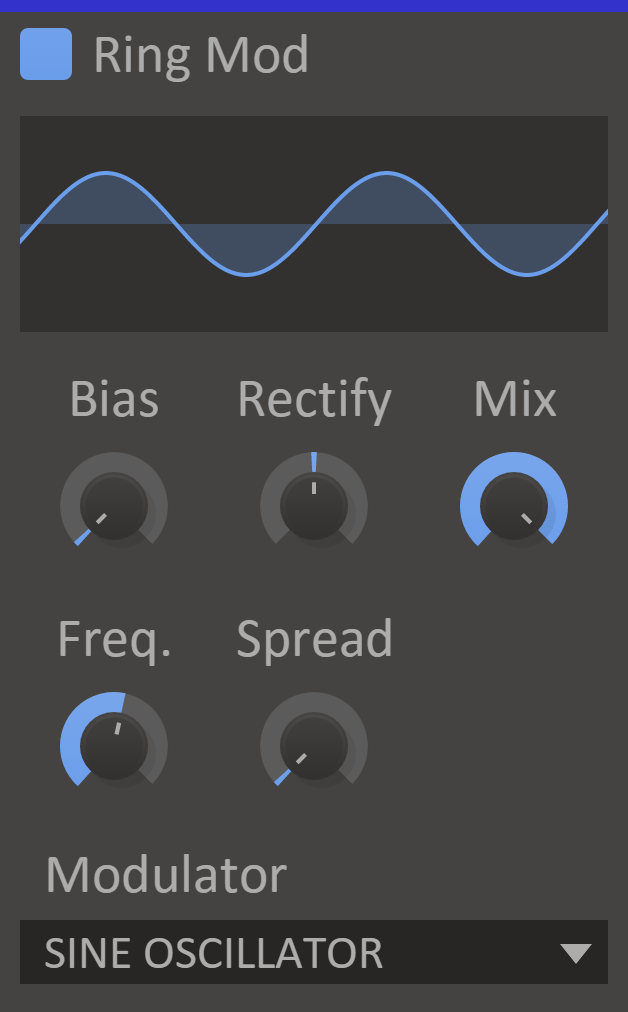
Ring Mod
A ring modulator gets its name from the way the original analog schematic used a ring of diodes to multiply two signals together. Honestly, the schematics are more of a square, but who cares when you can trash your sound beyond recognition in both pleasant and horrible ways?
Ring Mod uses either an internal sine/noise generator or a secondary input as the second signal in the modulation and allows for a versatile transformation of the modulating signal.
Features
- Bias Knob - Amount of positive bias to add to the secondary input.
- Rectify Knob - Amount of positive or negative rectification to apply to the secondary input.
- Frequency Knob - The base frequency of the internal oscillator or filter cutoff for the internal noise generator.
- Spread Knob - Shifts the frequency of the internal generator slightly for left and right channels to achieve a stereo effect.
- Modulator - Selects the secondary input.
- Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
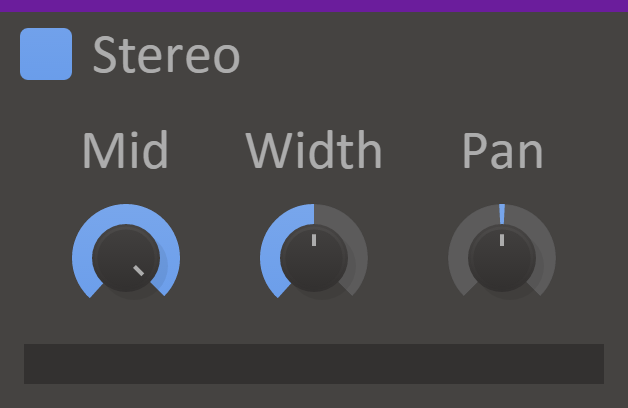
Stereo
Left speaker. Right speaker. W i d e and Narrow
That's what this plugin does. Questions?
(The Stereo snapin can adjust the stereo width and panning. It also displays the current balance and channel correlation visually.)
Features
- Width Knob - Adjusts the stereo width. The input audio must have at least a little stereo information for this knob to do anything.
- Pan Knob - Adjusts the panning.
- Mid Knob - Controls how much of the non-stereo content to let through.
- Stereo Meter - Displays the current balance and channel correlation. When the meter moves into the red area the correlation is less than zero, which can cause problems with mono compatibility.
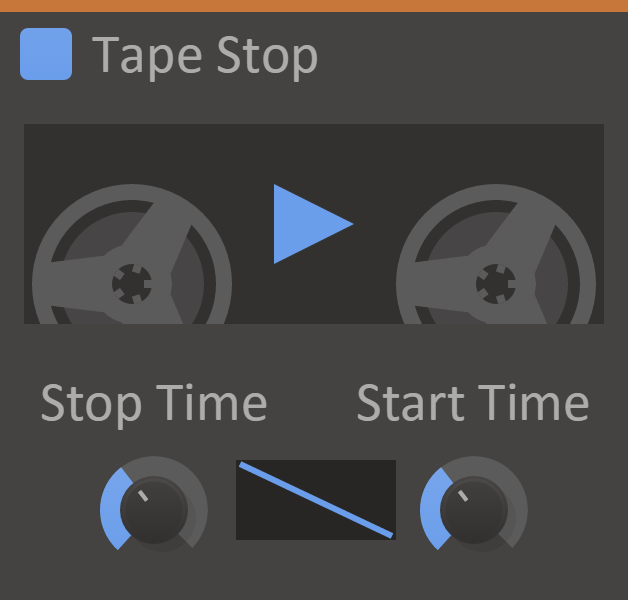
Tape Stop
At about the same time as dinosaurs roamed the earth, magnetic tape was the hottest way to store recorded audio. Naturally, cavemen discovered that starting and stopping the tape while playing back would lead to interesting effects.
Tape Stop simulates this arcane technology in a simple way, allowing you to get great spindown/speedup sounds quickly with the push of a button. What's next? Harnessing the power of fire?
Features
- Play Button - The current state of the tape motor.
- Stop Time Knob - Time until the tape motor reaches full stop when stopping.
- Start Time Knob - Time until the tape motor reaches full speed when starting.
- Curve - The speed curve of the tape motor starting/stopping.
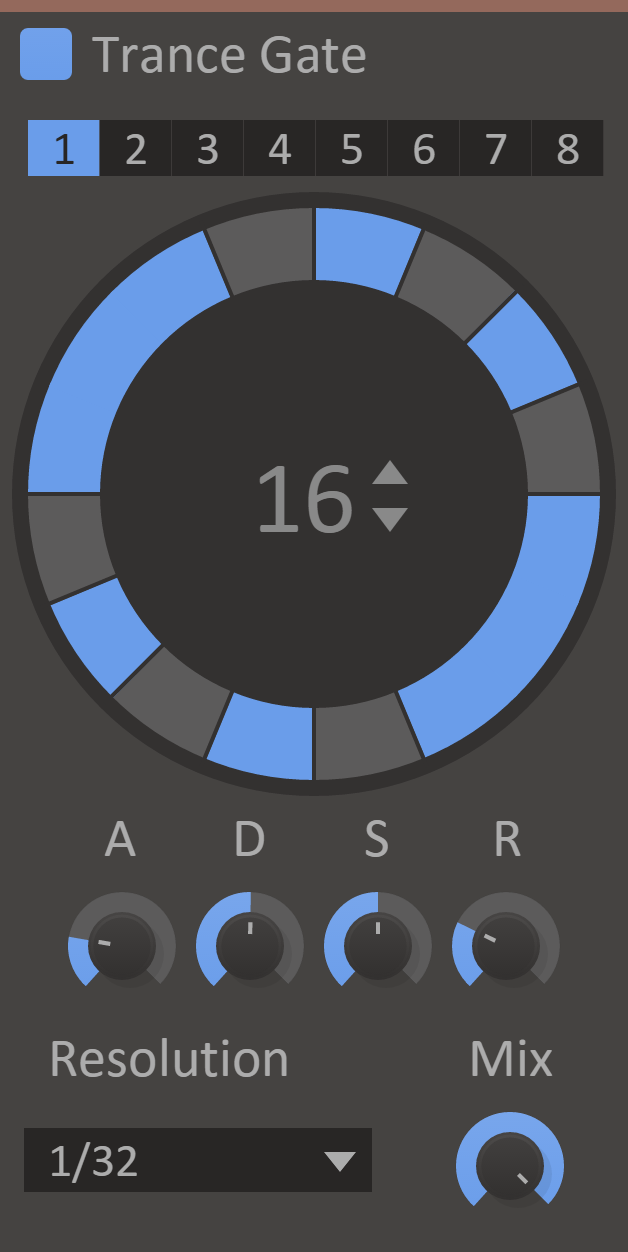
Trance Gate
What if ___ _____ easily chop up ____ __ the sound __ _ rhythmical pattern?
Well, now you can! Trance Gate is a gate sequencer which quickly adds a rhythm to a pad or lead, chops up a beat or adds more staccato to an arpeggio.
The world of anthem trance lies at your feet!
Features
- Pattern Select - Switches between the eight different pattern slots.
- Pattern Editor - Edits the current pattern. Click to toggle steps on or off, and click and drag to tie steps together.
- Length Display - The length of the current pattern.
- Attack, Decay, Sustain and Release Knobs - These knobs control the ADSR envelope which is applied to your sound, using the specified pattern.
- Resolution - Length of one step in the sequencer.
- Mix - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
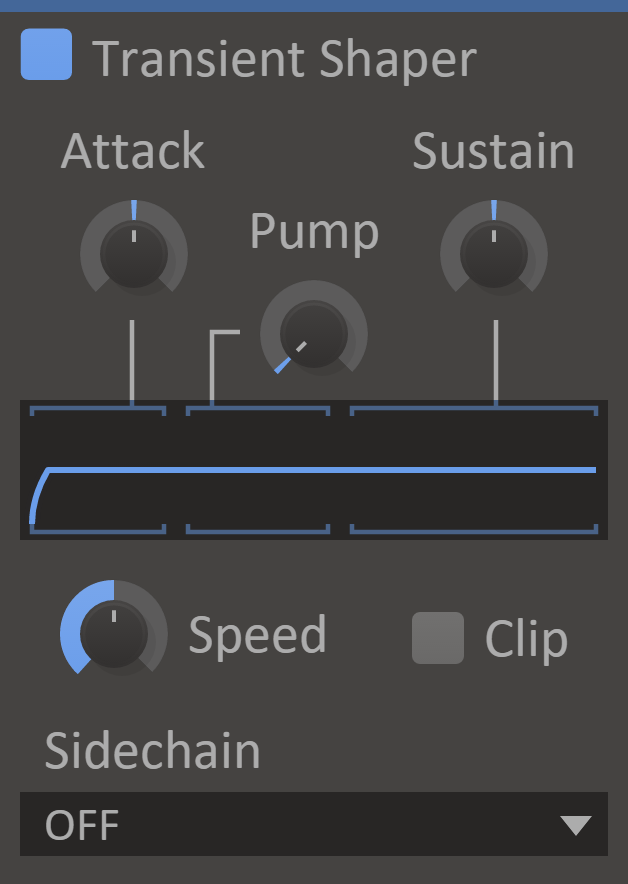
Transient Shaper
Customize attack character with Transient Shaper.
When you want to carefully tweak the punch of your snare, the ricki-ticki-ticking of your hi-hats or the snappiness of a synth line, Transient Shaper is the right tool for the job.
Using a compressor is the most common way of adjusting the dynamics of a sound, but sometimes this can be a bit cumbersome. This is where Transient Shaper shines, giving you very direct control over the character of both the attack and sustaining sections of the sound in a way that's simple to understand and tweak.
Features
- Attack - The amount of amplification or attenuation of the transient.
- Pump - The amount of attenuation directly after the transient, emphasizing the transient without increasing the level.
- Sustain - The amount of amplification or attenuation of the sustained sound.
- Clip - When enabled, the output signal is clipped to 0dB.
- Sidechain - When enabled transients are detected based on a secondary input, but the effect is applied to the main input.
- Speed - Higher values result in snappier transient modification, and lower values result in smoother curves.
Channel Mixer

Stereo and Phase Utility
Precise control over stereo content can be very useful. Phase inversion, swapping left and right, and various mid/side operations are among the many uses of Channel Mixer. Make sure to check out the presets of this little utility Snapin to get a good understanding of what it's capable of.
Left to Left
Scales the amplitude of the incoming left stereo channel from -1 (phase inverted) through 0 (silent) to 1 (passthrough).
Right to Left
Scales the amplitude of the incoming right stereo channel, but outputs it to the left channel.
Left to Right
Scales the amplitude of the incoming left stereo channel, but outputs it to the right channel.
Right to Right
Scales the amplitude of the incoming right stereo channel, and outputs it to the right channel.
Dual Delay
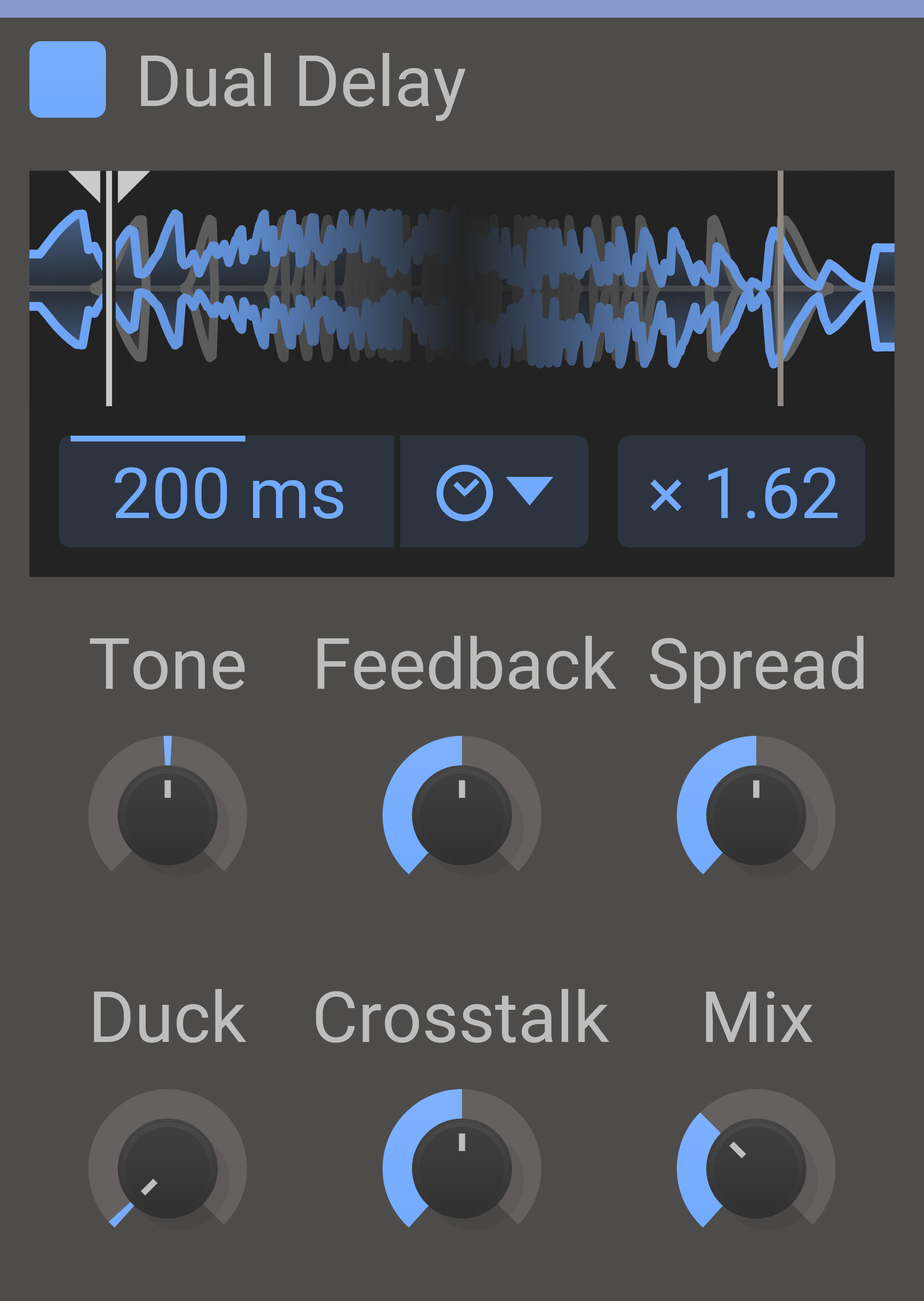
Crossfeeding Echoes
Dual Delay is like a regular delay that wants to be a reverb and ends up being something cool and new instead, with its double delay lines working in tandem to give you rich and complex echoing systems in seconds.
As with all Kilohearts Snapins, hooking them up to the amazing modulation options available in our host plugins gives you oodles of extra sound design flexibility.
Features
Delay Time - The amount of time before the delayed sound starts playing. This will be expressed in milliseconds or as parts of a beat, depending on Sync Mode.
Tone Knob - Applies a shelf filter on the delayed signal to gently shape the characteristic of the "echo".
Feedback Knob - Will cause the delayed sound to feed back into the delay. This will create an exponentially decaying echo.
Duck Knob - When duck is turned up, the output volume from the delay will automatically be lowered when the input volume is high.
Multiplier - The amount of time before the secondary delayed sound starts playing, expressed as a multiple of the primary delay time.
Spread Knob - Pans the delay taps altering between left and right.
Crosstalk Knob - The amount of "bleeding" between the two delay lines.
Mix Knob - The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Shaper
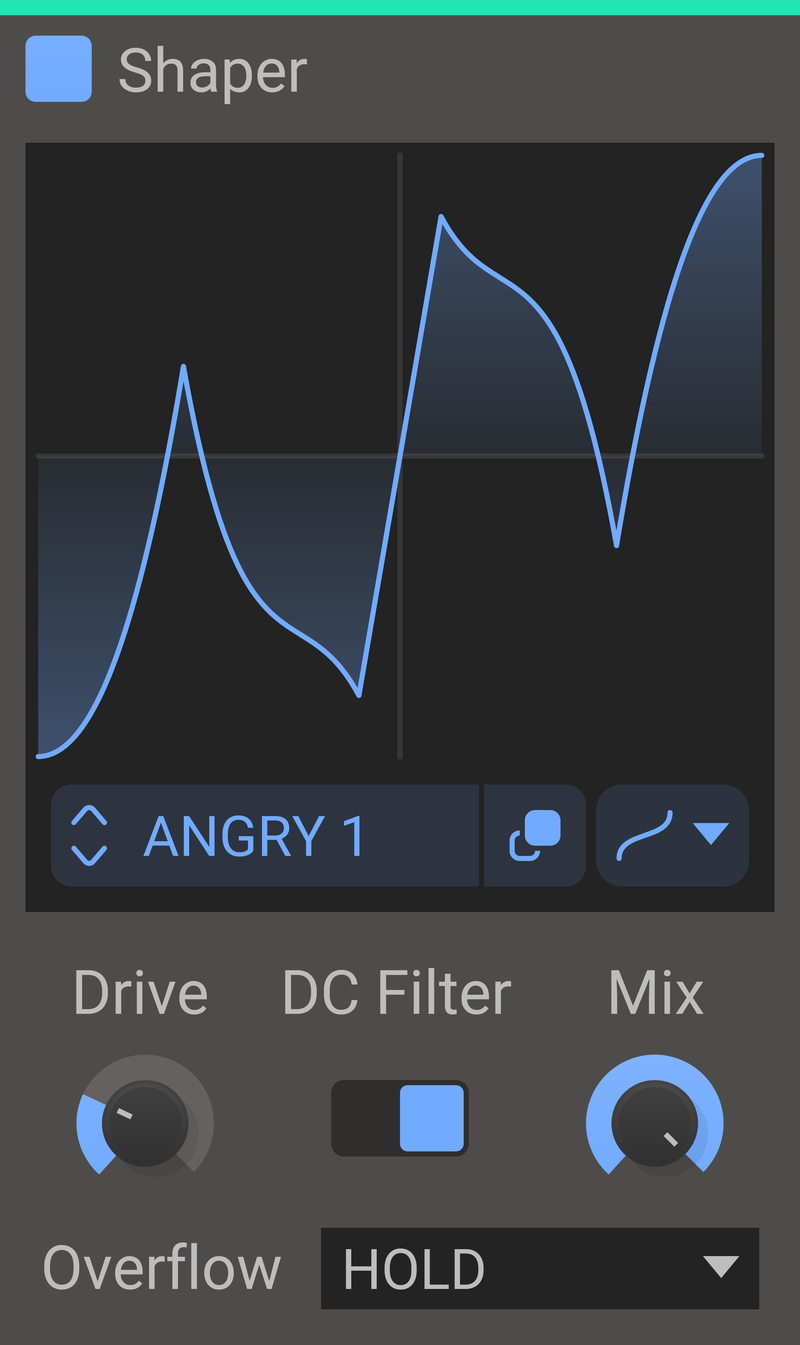
Wikipedia says:
"The sound produced by digital waveshapers tends to be harsh and unattractive, because of problems with aliasing"
Well. They clearly never listened to Kilohearts Shaper. A little bit of black magic trickery and any aliasing is kept to a minimum. Get all your distortion needs met with your own custom distortion shapes, or choose any shape from the included factory library.
Features
- Graph: A visualization of the remapping of the audio.
- Remap selector: Selects a remap from the Remaps browser. Click the popup button to open the big editor.
- Drive knob: The drive setting will boost the input signal, causing a heavier distortion.
- DC Filter: Enables a DC filter that fixes any DC offset introduced by the distortion.
- Mix: The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Overflow modes: Select what happens beyond the edges of the wave shape curve. Repeat the wave, hold the edge value, or repeat with mirroring.
System Requirements
These are the minimum recommended system requirements for running snapins.
Operating System:
- Any version of Windows or MacOS actively maintained by Microsoft or Apple.
CPU
- 2 GHz or faster
Memory
- 1 GB or more
Supported Software
- Any DAW supporting VST 2, VST 3, AAX, or Audio Unit plugin standards
Important Notes
- Kilohearts recommend keeping up to date with OS versions as they become available.
- Kilohearts is not able to support OS versions that are no longer supported by their respective manufacturers.
- If you are using an outdated OS please try the demo versions to ensure compatibility before making any purchases.
Any references to any brands on this site/page, including reference to brands and instruments, are provided for description purposes only. For example references to instrument brands are provided to describe the sound of the instrument and/or the instrument used in the sample. Plugin Boutique do not have (nor do they claim) any association with or endorsement by these brands. Any goodwill attached to those brands rest with the brand owner. Plugin Boutique or its Suppliers do not accept any liability in relation to the content of the product or the accuracy of the description. "RHODES" is a registered trademark of Joseph A Brandstetter.